Objectives
A quick guide on how to disable Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) in any RPM-based distributions (CentOS, RedHat, RHEL and etc).
Prerequisites
- A virtual machine with any RPM-based distro installed.
Steps
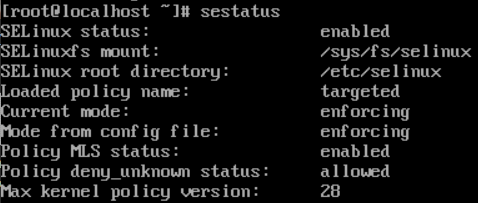
Step 1: Check Current Status
To check the current status of SELinux, simply enter the following command: –
sestatus
Sample Output: –
Step 2: Edit Config file to Disable SELinux
Next, you can use the nano text editor to modify the /etc/selinux/config file.
nano /etc/selinux/config
Change the value from enforcing to disabled.
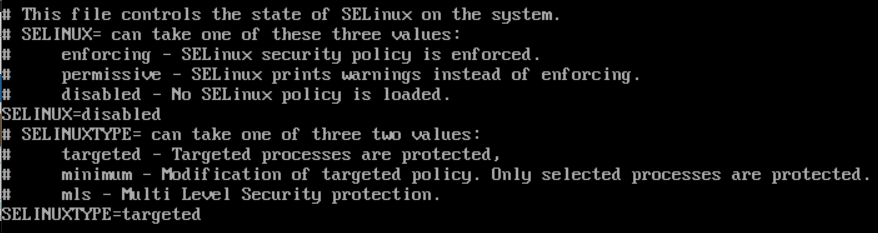
Save and exit the editor.
Alternatively, if you wish to disable / enable SELinux temporarily, you can use setenforce command.
setenforce Enforcing / Permissive / Disabled
Step 3: Verify Your Changes
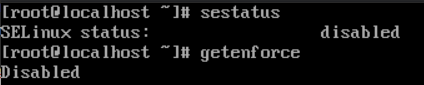
Reboot the server and check the status of SELinux to see if it is disabled.
sestatus OR getenforce